Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is one of the most important
chemical processes which enable our bodies to fully utilize
THC and
CBD and their benefits.

Cannabis plant does not produce Δ
9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD). It actually makes
Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and
cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), which have not been proved to induce psychoactive effects, such as the “high” feeling from THC. THCA and CBDA are converted to THC and CBD respectively by a process called
decarboxylation, in which these compounds are chemically changed and have a by-product of carbon dioxide gas (CO
2) (see Figures 1 and 2).
1 This is accomplished when THCA and CBDA are heated, either when being smoked/vaped or during extraction into edible ingredients, for example by heating oil with cannabis while making brownies.
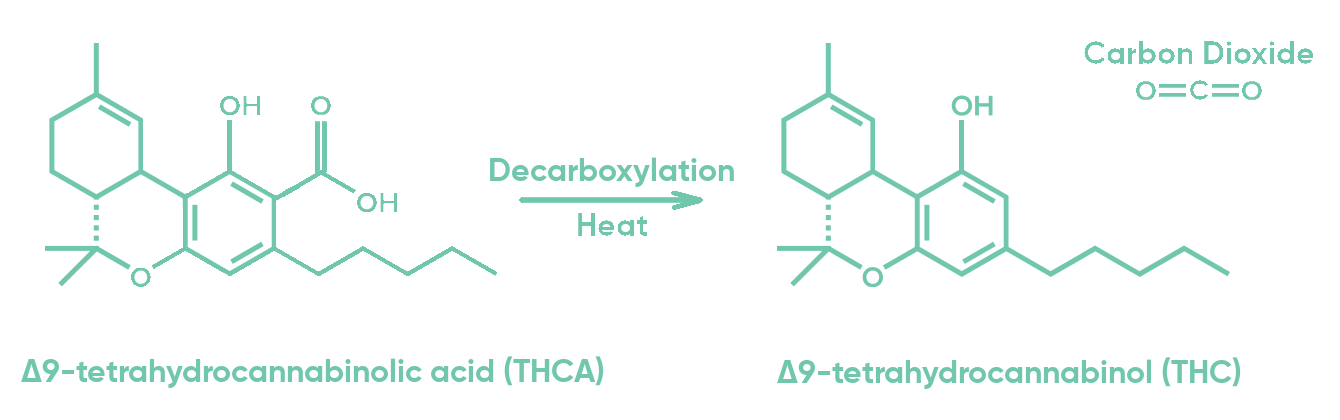 Figure 1: The transformation of THCA molecule into THC + CO2.
Figure 1: The transformation of THCA molecule into THC + CO2.
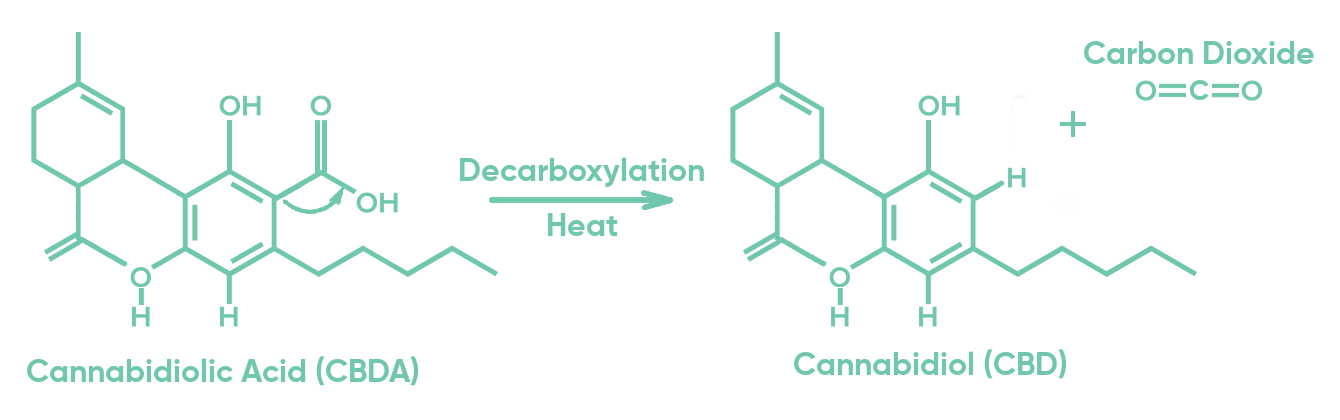 Figure 2: The transformation of CBDA molecule into CBD + CO2.
Figure 2: The transformation of CBDA molecule into CBD + CO2.
- Veress, T.; Szanto, J. I.; Leisztner, L. (1990). Determination of cannabinoid acids by high-performance liquid chromatography of their neutral derivatives formed by thermal decarboxylation: I. Study of the decarboxylation process in open reactors. Journal of Chromatography A, 520(Supplement C), 339--347.
 Cannabis plant does not produce Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD). It actually makes Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), which have not been proved to induce psychoactive effects, such as the “high” feeling from THC. THCA and CBDA are converted to THC and CBD respectively by a process called decarboxylation, in which these compounds are chemically changed and have a by-product of carbon dioxide gas (CO2) (see Figures 1 and 2).1 This is accomplished when THCA and CBDA are heated, either when being smoked/vaped or during extraction into edible ingredients, for example by heating oil with cannabis while making brownies.
Cannabis plant does not produce Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD). It actually makes Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), which have not been proved to induce psychoactive effects, such as the “high” feeling from THC. THCA and CBDA are converted to THC and CBD respectively by a process called decarboxylation, in which these compounds are chemically changed and have a by-product of carbon dioxide gas (CO2) (see Figures 1 and 2).1 This is accomplished when THCA and CBDA are heated, either when being smoked/vaped or during extraction into edible ingredients, for example by heating oil with cannabis while making brownies.
 Figure 1: The transformation of THCA molecule into THC + CO2.
Figure 1: The transformation of THCA molecule into THC + CO2.
 Figure 2: The transformation of CBDA molecule into CBD + CO2.
References:
Figure 2: The transformation of CBDA molecule into CBD + CO2.
References:_logo.svg)